The chance of dying from a TBE infection can range from less than 2% – 40%, dependent on which type of infection you get.2
Disease video
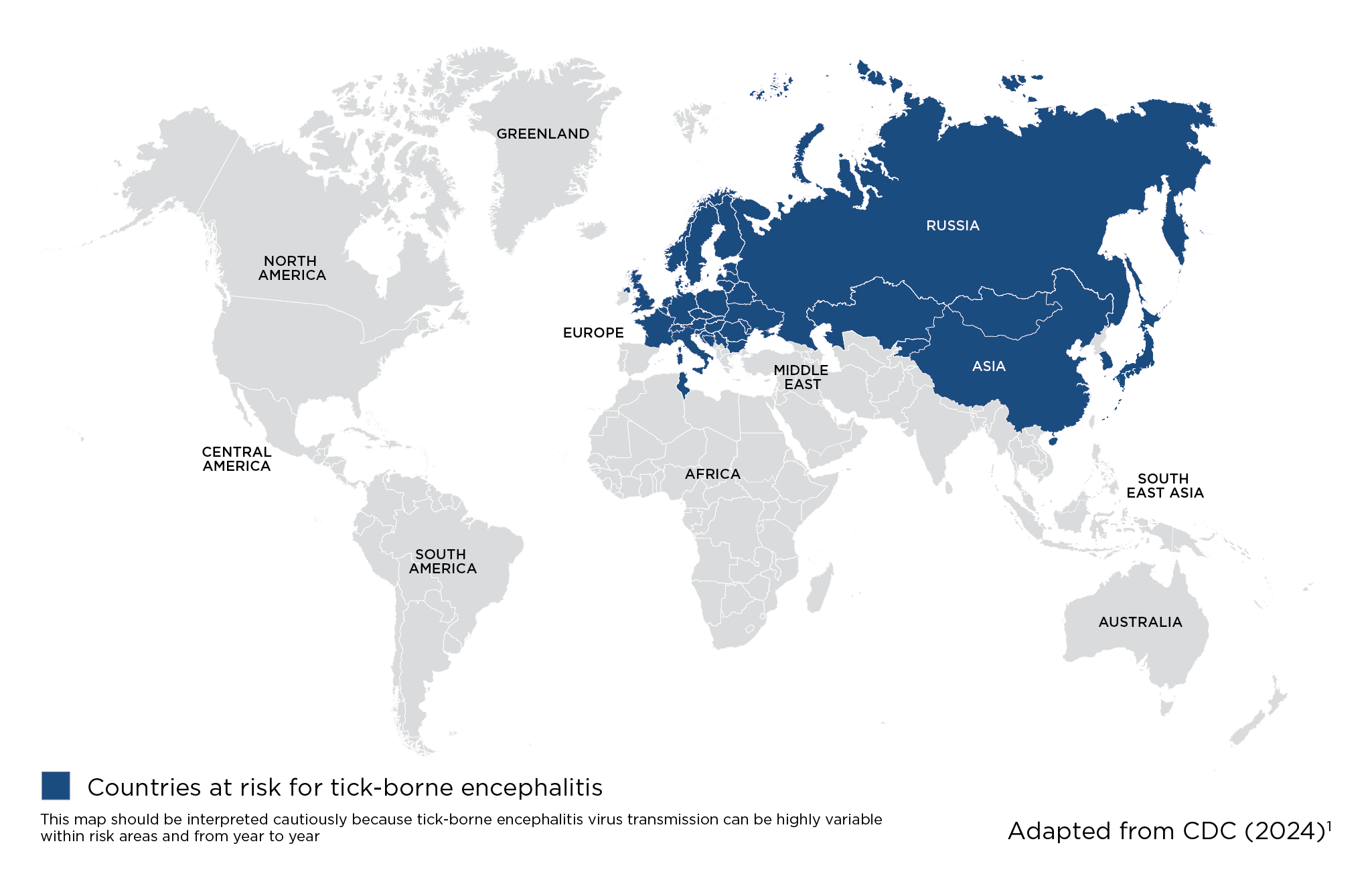
Risk areas for Tick-Borne Encephalitis
FAQs
-
Key fact
-
How do you get tick-borne encephalitis?
Being bitten by a tick carrying the virus which causes the disease or by ingesting unpasteurised dairy products (such as milk and cheese) from infected animals.2
-
Which countries are affected by tick-borne encephalitis?
Tick-borne encephalitis found in many countries in Europe and Asia (see map). There is greater risk in forested areas.2
-
What are the symptoms of tick-borne encephalitis?
Many TBE infections do not show any symptoms. If symptoms do occur, this can take up to 28 days and may include nausea, fever, headache, muscle pain or tiredness.2,3
-
How serious is tick-borne encephalitis?
Most people recover fully, but in a few cases, infection leads to inflammation of the tissue surrounding the brain (meningitis) and the brain itself (encephalitis). When this happens, symptoms can include confusion, difficulty with speech, weakness or loss of movement in parts of the body and seizures.2,3
-
Can I prevent getting tick-borne encephalitis?
You can take the following precautions to help reduce your risk of infection:
- Visit your nearest convenient pharmacy or specialist travel health clinic for a risk assessment before your trip
- Avoid places – like long grass – where ticks live3,4
- Use a recommended insect repellent containing either Picaridin, DEET, PMD or OLE (oil of lemon eucalyptus), IR3535 or 2-undecanone4
- Wear appropriate clothing (e.g long-sleeved clothes, long trousers, socks and shoes) to minimise exposed skin4
- Regularly check for ticks that may have attached themselves to your body.3 Carefully remove any that you find using a tick remover or tweezers. Gently grip the tick as close to the skin as possible and pull it upwards without twisting or crushing. Then wash your skin with water and soap and apply an antiseptic cream.3,4
Ready to get started? Check now for your nearest travel health clinic.
Get friendly advice from the UK's largest network of travel clinics*.
* This list is not exhaustive and other travel health providers are available.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Areas at Risk for Tick-borne Encephalitis. May 2024. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/tick-borne-encephalitis/data-maps/ (Last accessed May 2025)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Yellow Book 2026. Travel-Related Infections & Diseases. Tick-Borne Encephalitis. April 2025. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/yellow-book/hcp/travel-associated-infections-diseases/tick-borne-encephalitis.html (Last accessed May 2025)
- NHS Choices. Conditions. Tick-borne Encephalitis. July 2024. Available online:
http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/tick-borne-encephalitis/ (Last accessed May 2025) - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Yellow Book 2026. Environmental Hazards & Risks. Mosquitoes, Ticks & Other Arthropods. April 2025. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/yellow-book/hcp/environmental-hazards-risks/mosquitoes-ticks-and-other-arthropods.html (Last accessed May 2025)
UK-BOTB-2500016 May 2025
